Machine Learning Directed Study: Report 2
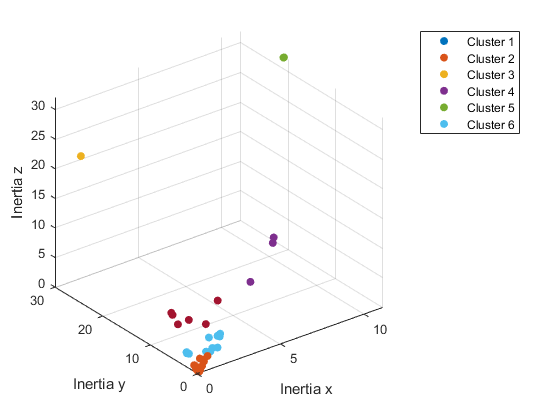
Anson’s Projects focuses on a machine learning directed study where 3D models of satellite assemblies are utilized to simulate debris data. The models, sourced from GrabCAD, were processed using Blender to create 108 unique parts. An algorithm implemented in Julia calculates essential properties like moments of inertia and volume, which are critical for analyzing debris characteristics. The dataset is normalized based on volume to ensure consistency across data science algorithms. Principal component analysis (PCA) is employed to identify key properties that explain data variation, revealing that the largest moment of inertia is most significant. K-means clustering is used to categorize the data into six clusters, highlighting the presence of outliers associated with various shapes of debris. The study emphasizes the need to expand the dataset in both quantity and variety, particularly by incorporating actual debris samples. Future efforts will also focus on deriving additional properties to enhance analysis. Overall, the project aims to advance understanding of satellite debris characteristics and improve data processing efficiency.
This content was originally posted on my projects website here. The above summary was made by the Kagi Summarizer
